
LAKE MEAD, NV (31 December 2019) — The weather looked good in the morning and I set off on the quickest route to Lake Mead, where I decided to set up my camp for New Years Eve. It was a long drive and in the mountains there was still snow. Made it to camp in time to catch the last sunset of 2019 from my perfect spot on the edge of the campsite facing the lake and mountains beyond. As I settled into the warmth of my fire an unseen chorus of coyotes marked the night.

ABOUT THE EXPEDITION
JoMarie Fecci, of USnomads, sets off on the first holiday roadtrip with the new Jeep, overlanding from New York to the deserts of the southwest. Once out in the desert, it will be time for some scouting and pre-running in preparation for an upcoming adventure. The primary goal of this journey is to get the Jeep pre-positioned in the west, and to assess terrain, logistical concerns and approximate timeframes for future travel.
WHERE WE ARE
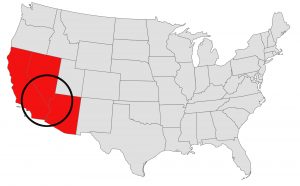
There are four deserts that connect across the southwest of the United States — the Great Basin, Mojave, Sonoran and Chihuahuan. The Great Basin Desert is “high desert” which can get cold and see much snow in winter. This desert covers southeast Oregon, a small portion of northeast California, most of west Utah, part of southeast Idaho, and the majority of Nevada – all except the southernmost 150 miles which are within the Mojave Desert. All this land is characterized by long, thin, parallel mountain ridges running north-south, separated by wider valleys, often containing dry lake beds (playas) or salt basins. The few rivers run inwards, with no outlet to the ocean; their waters ultimately either sink below ground or evaporate. The Mojave Desert covers the southernmost 150 miles of Nevada, a tiny area of southwest Utah, lower elevation regions of northwest Arizona (bordering the Colorado River) and most of southeast California. The topography is generally similar to the Great Basin, with isolated mountains and wide, flat plains, but temperatures are hotter, vegetation sparser, and the hills are less numerous. The Sonoran Desert of southwest Arizona and the south-eastern tip of California has perhaps the most archetypal desert scenery in the Southwest, with vast flat plains and abundant cacti, especially the giant saguaro, which occurs most densely in Arizona towards the higher elevation reaches of the desert, between 1,500 and 3,500 feet. The Sonoran desert continues a long way south into Mexico, nearly 500 miles down the east side of the Gulf of California. The Chihuahuan Desert is the second largest in the US, and also extends a long way into Mexico. It covers the southern third of New Mexico, excluding several mountain ranges, and all of far west Texas, west of a line between Del Rio and Monahans. Elevations are generally higher than in the Sonoran Desert (2,000 to 6,000 feet), and precipitation is a little greater, with most rain falling during the summer thunderstorm season. Cacti are still quite numerous but are generally smaller than to the west; instead, the dominant plants are yucca and agave, though even so, as with many other desert regions, large areas have only the ubiquitous creosote bushes and mesquite trees. For more information and a list of interesting places to visit in each desert see the American Southwest website.